Nondestructive testing is to use the characteristics of sound, light, magnetism and electricity to detect whether there are defects or inhomogeneity in the tested objects without damaging or affecting the performance of the tested objects, Give the size, location, nature and number of defects and other information, and then determine the technical status (such as qualified or not, residual life, etc.) of the object to be inspected. Common non-destructive testing methods: ultrasonic testing (UT), magnetic particle testing (MT), liquid penetration testing (PT) and X-ray testing (RT).
The Main Role of Nondestructive Testing:
1. Non-destructive testing: To evaluate the quality of products, whether it is forgings, castings, welded steel structures, sheet metal or machined parts or even non-metallic structures, non-destructive testing technology can be used to identify their surface or internal defects, and the defects can be qualitatively or quantitatively analyzed.
2. Material inspection: Non-destructive testing technology can be used to determine the physical properties, mechanical properties and internal structure of materials, to distinguish the varieties of materials and heat treatment status, and to separate mixtures.
3. Geometric measurement: The geometric size of the product, coating or coating thickness, surface corrosion state, hardening depth and stress-strain state can be measured by non-destructive testing technology.
4. On-site monitoring: The product in service or production can be dynamically detected on-site, and the defect change information of the product can be continuously provided to the detection, so as to implement monitoring.

The following is a brief introduction and comparison of the four detection methods.
ultrasonic testing (UT):Ultrasound flaw detection is a method to inspect the defects of parts by means of the reflection characteristics of the interface edge when the ultrasonic energy penetrates deep into the metal material and enters another section from one section. The ultrasonic beam emitted by the probe penetrates through the metal interior from the surface of the part, when the defect and the bottom of the part are encountered, the reflected wave will occur separately, then pulse waveform will be formed on the fluorescent screen. The position and size of the defect can be judged by these pulse waveforms.
The advantages of the ultrasonic detection method are as follows:
1. For example, the effective detection depth in steel can reach more than 1 meter.
2. For planar defects such as cracks and sandwiches, the detection sensitivity is high, and the depth and relative size of defects can be measured.
3. The equipment is portable, safe to operate and easy to realize automatic inspection.
The disadvantages are:
1. For complex workpiece, it is not easy to detect. It requires a certain degree of smoothness of the inspected surface and a coupling agent to fill the gap between the probe and the inspected surface to ensure adequate acoustic coupling
2. For some coarse grained castings and welds, it is difficult to apply them because they are easy to produce cluttered reflection waves. In addition, ultrasonic testing also requires experienced inspectors to operate and judge the test results.
Magnetic particle testing: It is to use the difference of permeability between defective areas (surface defects and near-surface defects, such as cracks, slag inclusions, hairlines, etc.) and non-defective areas in iron and steel products. After magnetization, the magnetic field in discontinuous areas (defective areas) of these materials will be distorted, resulting in the surface of part of flux leakage. The magnetic flux leakage field is used to attract the accumulation of magnetic powder at the defect, which is called magnetic trace. Under appropriate illumination conditions, the location and shape of the defect are displayed. The accumulation of these magnetic particles is observed and explained, and the magnetic particle inspection is realized.
The applicability and limitations of magnetic particle testing are as follows:
1. Magnetic particle inspection is suitable for detecting discontinuity on the surface and near surface of ferromagnetic materials with very small size and very narrow gap
2. Magnetic particle testing can be used to detect parts and components in various situations, as well as various types of parts.
3. Cracks, inclusions, hairlines, white spots, folding, cold isolation and looseness can be found.
4. The magnetic powder test can not detect the welds of austenitic stainless steel materials and austenitic stainless steel electrodes, nor can it detect non-magnetic materials such as copper, aluminium, magnesium and titanium. It is difficult to find the layers and folds with shallow scratches, deep buried holes and angles less than 20 degrees to the workpiece surface.
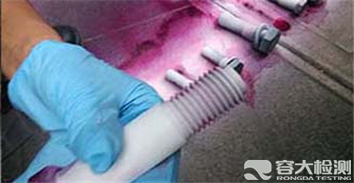
Penetration testing :Penetration testing is to coat a dye-containing dye or fluorescent penetrating agent on the surface of parts. Under capillary action, due to the wetting of liquid and capillary action, penetrating agent penetrates into surface opening defects. Then remove the excess penetrant on the surface of the part, and then coat the part with a thin layer of imaging agent. The penetrant in the defect is re-adsorbed to the surface of the part under capillary action to form an enlarged defect image display. The defect display is observed under black light (fluorescent test) or white light (coloring test)
The advantages of penetration detection are as follows:
1. It can detect all kinds of materials.
2. It has high sensitivity.
3. Visual display, easy operation and low detection cost.
The disadvantages of penetration detection are as follows:
1. It is not suitable for inspecting workpieces made of porous loose materials and workpieces with rough surface.
2. Permeation detection can only detect the surface distribution of defects, and it is difficult to determine the actual depth of defects, so it is difficult to make quantitative evaluation of defects. The detection results were also greatly affected by the operator.
Radiographic testing: The principle of X-ray detection is that X-ray will be lost when it passes through the irradiated object. The absorptivity of different materials with different thicknesses is different, when the negative is placed on the other side of the irradiated object, the corresponding figure will be produced because of the different intensity of the radiation, the reviewer can judge whether there are defects in the object according to the image, and the nature of the defect.
Applicability and limitations of X-ray detection:
1. It is sensitive to detect the defect of volume type and easy to identify the defect.
2. X-ray film is easy to preserve and has traceability.
3. It is intuitive to show the shape and type of defects.
4. The disadvantage is that it can not locate the burial depth of the defect, and the thickness of the detection is limited. The film needs to be sent and washed specially, which is harmful to the human body and has a high cost.
In a word, ultrasonic and X-ray
flaw detection are suitable for internal flaw detection; Ultrasound is suitable
for parts with regular shape and more than 5mm; X-ray can't locate the depth of
the defect, and having radiation. Magnetic powder and penetration testing are
suitable for surface defects of flaw detection parts. Among them, magnetic
particle testing is limited to the detection of magnetic materials, and
penetration testing is limited to the detection of surface opening defects.
Non-destructive inspection of weld seam is very important for building steel structure manufacturing, welding structural parts, pressure vessels, shipbuilding, metallurgy and other equipment manufacturing. It is also an important means to ensure the quality of weld seam.

